|
Brief Description
|
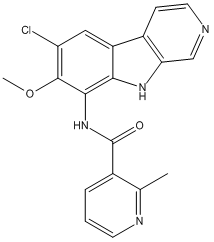
MLN120B is a potent and effective IKKbeta inhibitor.
IC50 Value: MLN120B (20 umol/L) induced up to 35% and 75% inhibition, assessed by MTT assay and [3H]thymidine uptakein multiple myeloma cell lines, respectively.
Target: IKKbeta
NF-κB pathway blockers, such as MLN120B, are currently being explored for treatment of inflammatory diseases such as COPD and asthma.
in vitro: MLN120B inhibits both baseline and tumor necrosis factor-α-induced nuclear factor-κB activation, associated with down-regulation of IκBα and p65 nuclear factor-κB phosphorylation. MLN120B triggers 25% to 90% growth inhibition in a dose-dependent fashion in multiple myeloma cell lines and significantly augments tumor necrosis factor-α-induced cytotoxicity in MM.1S cells. MLN120B augments growth inhibition triggered by doxorubicin and melphalan in both RPMI 8226 and IL-6-dependent INA6 cell lines. Neither IL-6 nor IGF-1 overcomes the growth-inhibitory effect of MLN120B. MLN120B inhibits constitutive IL-6 secretion by BMSCs by 70% to 80% without affecting viability. Importantly, MLN120B almost completely blocks stimulation of MM.1S, U266, and INA6 cell growth, as well as IL-6 secretion from BMSCs, induced by multiple myeloma cell adherence to BMSCs.
in vivo: MLN120B mediates anti-human multiple myeloma cell activity in vivo using a novel SCID-hu model, in which multiple myeloma cells grow in vivoin the context of the human bone marrow microenvironment. Eight SCID mice were implanted with human fetal bone chips (SCID-hu), into which human IL-6-dependent INA6 cells were directly injected. These mice were treated orally with either MLN120B (50 mg/kg) or vehicle control twice daily for 3 weeks. Oral administration of ML120B inhibited paw swelling in a dose-dependent manner (median effective dosage 12 mg/kg twice daily) and offered significant protection against arthritis-induced weight loss as well as cartilage and bone erosion.
|